Differential Gear
A differential gear, also called diff gear, is a set of gear combinations, usually including planetary gears, sun gears, and rings, that form the core of a differential. It distributes input power to multiple output shafts through the interaction of the gears and allows these shafts to rotate at different speeds. GBC offers high-quality various types of differential gears for sale. Contact us if you are interested!
Differential Gear Unit Function
Compensation for Speed Difference When Turning
When a vehicle is turning, the outer wheels have a longer travel path than the inner wheels, so the outer wheels need to turn faster. The car differential gears ensure smooth cornering by distributing the power so that the left and right wheels rotate at different speeds.
Improves Traction and Stability
Automobile differential gears distribute engine power to the wheels, preventing a single wheel from slipping and improving vehicle handling and stability in different road conditions.
Reduces Tire Wear
By allowing the wheels to rotate at their natural speeds, the differential gear reduces friction between the tires and the ground, extending tire life.
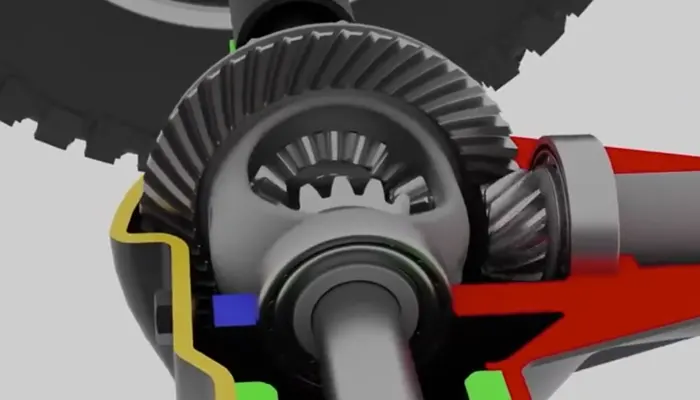
Differential Gear Parts
Differential Planetary Gears:
These pinions are located inside the differential, usually 2-4 of them, and are mounted on the planetary gear carrier. They mesh with the side gears and are responsible for transmitting and distributing power.
Differential Side Gears:
Differential side gears, also called differential sun gears are attached to the left and right axles (half shafts) and transmit power to the wheels. The side gears mesh with the planetary gears and allow the wheels on each side to rotate at different speeds.
Planetary Gear Carrier:
The carrier holds the planetary gears in place and is driven by the drive shaft (from the transmission). The planetary gear carrier is the carrier of the power input.
Differential Case:
The differential case wraps around all internal gears, protecting and supporting the entire differential structure.
Differential Ring and Pinion Gear:
Fixed to the differential case, the differential ring gear (crown gear) meshes with the diff pinion gear on the drive shaft and receives the power from the transmission.
Working Principle of Differential Gear
The core of differential gear is to realize the differential rotation of left and right wheels through the relative motion of gears. The principle of operation is as follows:
When driving in a straight line:
The resistance of the left and right wheels is the same, and the planetary gears do not rotate, but only rotate with the planetary gear carrier around the main shaft. The power is equally distributed to the left and right wheels, and the wheels rotate at the same speed.
When turning:
The resistance of the inner wheel increases (shorter path) and the resistance of the outer wheel decreases (longer path). The planetary gears begin to rotate on their own, distributing more power to the outside wheel, causing it to rotate at a higher speed than the inside wheel.
This power distribution is realized by the meshing of the planetary gears with the side gears, and the differential automatically adjusts the speed difference between the two wheels.
Power Transmission:
The driveshaft transmits power through the pinion and drive gears to the differential housing, which rotates the planetary gear carrier, and ultimately the power is transmitted to the wheels via the planetary gears and side gears.
Types of Differential Gears
Differential gears can be categorized into the following common types based on their structure and function:
Open Differential
Characteristics: Open differential is the most common and simplest type of differential, allowing free differential between left and right wheels.
Advantages: simple structure, low cost, suitable for daily road driving.
Disadvantages: When one wheel slips (e.g., on icy or muddy roads), the power will flow completely to the slipping wheel, resulting in a loss of power to the other wheel, and the vehicle may get into trouble.
Applications: ordinary family cars, city SUVs, etc.
Limited-Slip Differential (LSD)
Characteristics: Partially locks the differential by limiting the speed difference between the wheels on both sides through a clutch, viscous coupling or gear design.
Advantage: Can still transfer part of the power to the wheels with grip in a skidding situation, improving traction.
Disadvantages: more complex structure, higher cost, may lead to less smooth handling when turning.
Applications: High-performance cars, off-road vehicles, racing cars.
Locking Differential
Characteristics: Can completely lock the differential, so that the left and right wheels rotate at the same speed.
Advantage: Provides maximum traction in extreme conditions (e.g. off-road).
Disadvantage: Poor maneuverability in corners, suitable for low speed or straight line driving.
Applications: Hardcore off-road vehicles (e.g. Jeep Wrangler), heavy trucks.
Torsen Differential
Characteristics: The full name is torque sensing, automatic torque distribution through worm gear structure.
Advantages: No need for clutches, fast response, dynamic distribution of torque, balance between performance and handling.
Disadvantages: Complex manufacturing and high cost.
Applications: High-end 4WD vehicles (e.g. Audi Quattro), sports cars.
Application Scenarios of Differential Gear
Maintenance and Precautions for Differential Gears
Check the lubricant regularly:
The internal gears of the differential require special gear oil lubrication, which is recommended to be changed periodically (usually every 30,000-50,000 kilometers) according to the vehicle manual.
Pay attention to abnormal noises:
If the differential makes abnormal noises (such as buzzing or clicking), the gears may be worn or insufficiently lubricated and need to be serviced promptly.
Avoid overloading:
Prolonged driving under high loads (such as off-roading or towing heavy loads) may cause the differential to overheat and shorten its life.
Choose the right differential:
Choose the right type of differential according to driving needs and avoid blindly pursuing high performance.
Contact Us
As the sales agent of Ever-power Group in Australia, GBC has always brought high-quality products to the market. The differential gear we provide is of excellent quality and stable performance. At present, this product has successfully covered multiple states such as New South Wales, Victoria, and Queensland. Its sales network spreads across major cities like Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane, and it can also be easily purchased in cities like Adelaide and Perth. Whether customers have demands in the local industrial or transportation-related fields, we can meet them.
